Thyroid disease affects millions of people worldwide, impacting energy levels, metabolism, and overall health. As conventional treatments like medication and surgery remain the cornerstone of managing thyroid disorders, complementary therapies such as acupuncture are gaining attention for their potential to alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life. This comprehensive guide explores thyroid disease, its causes, symptoms, and how acupuncture can serve as an effective treatment option, including key acupuncture points used in therapy.
What is Thyroid Disease?
The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland located in the neck, just below the Adam’s apple. It plays a critical role in regulating metabolism, heart rate, body temperature, and other vital functions through the production of thyroid hormones, primarily thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3). These hormones influence nearly every cell in the body, ensuring proper growth, development, and energy balance.
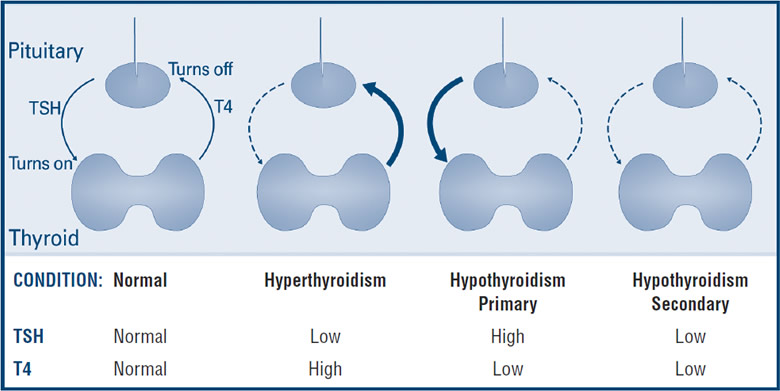
Thyroid disease occurs when the gland produces too much (hyperthyroidism) or too little (hypothyroidism) of these hormones, or when structural abnormalities like nodules or goiters develop. Below, we dive into the main types of thyroid disorders, their causes, and symptoms.
Types of Thyroid Disease
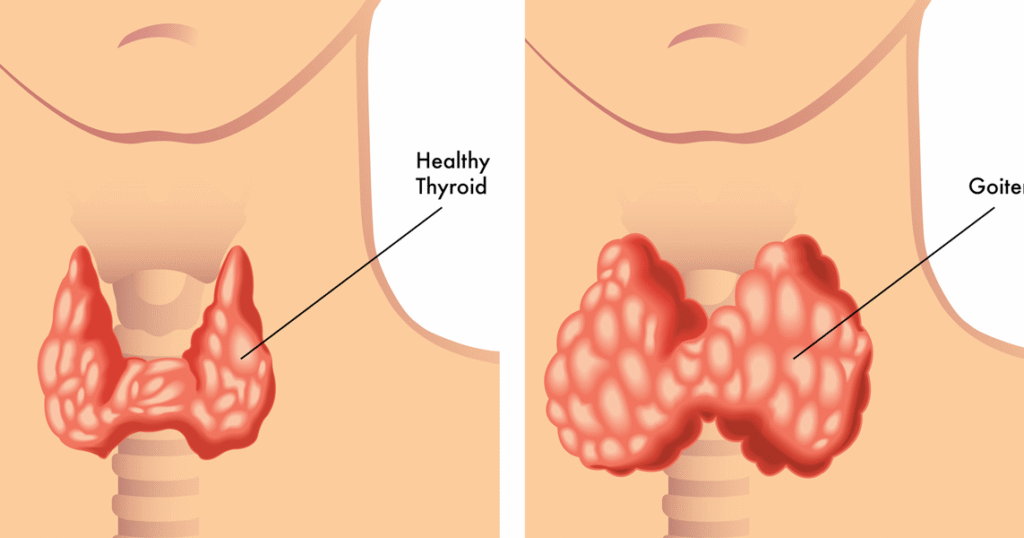
Hypothyroidism: This condition arises when the thyroid gland is underactive, producing insufficient hormones. Common causes include:
- Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis: An autoimmune disorder where the immune system attacks the thyroid, leading to inflammation and reduced hormone production.
- Iodine Deficiency: Iodine is essential for thyroid hormone synthesis, and its deficiency can impair gland function.
- Post-Surgical or Radiation Effects: Thyroid surgery or radiation therapy for other conditions can damage the gland.
- Medications: Certain drugs, like lithium, may interfere with thyroid function.
Symptoms of Hypothyroidism:
- Fatigue and lethargy
- Weight gain
- Cold intolerance
- Dry skin and hair loss
- Constipation
- Depression or brain fog
- Muscle aches and joint pain
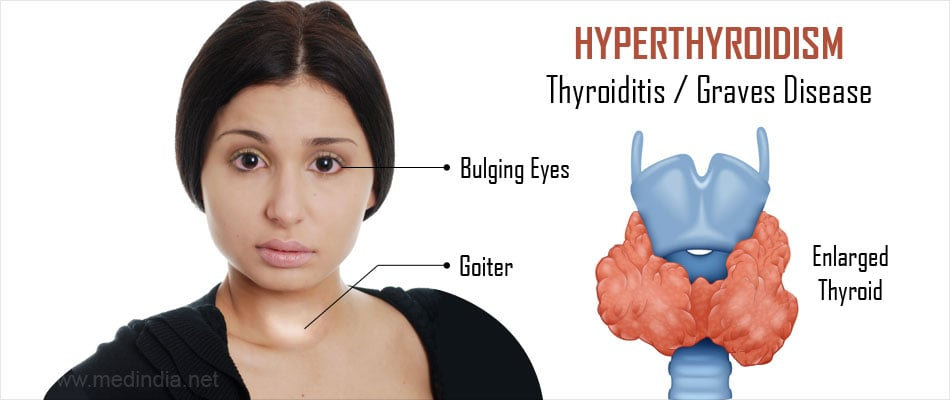
Hyperthyroidism: An overactive thyroid produces excessive hormones, speeding up bodily functions. Common causes include:
- Graves’ Disease: An autoimmune condition causing overstimulation of the thyroid.
- Toxic Nodules or Goiter: Benign lumps in the thyroid that produce excess hormones.
- Thyroiditis: Inflammation of the thyroid, sometimes causing a temporary surge in hormone levels.
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism:
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Weight loss despite increased appetite
- Nervousness, anxiety, or irritability
- Tremors or sweating
- Heat intolerance
- Insomnia
- Frequent bowel movements
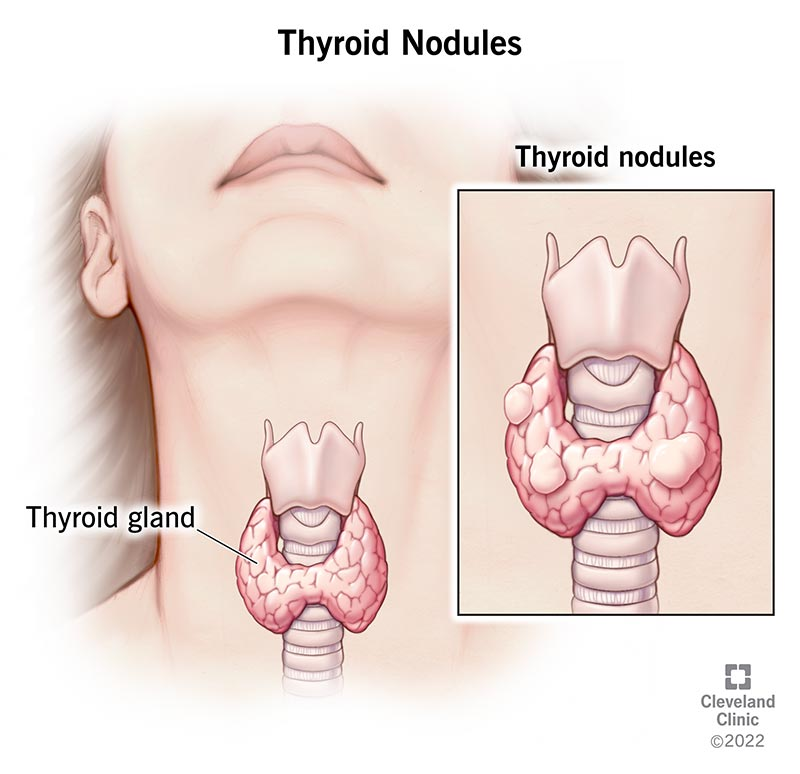
Thyroid Nodules and Goiter: These are structural abnormalities, such as lumps (nodules) or an enlarged thyroid (goiter). While often benign, some nodules may be cancerous or produce hormones, leading to hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid Cancer: Though less common, thyroid cancer is typically treatable when detected early. Types include papillary, follicular, medullary, and anaplastic thyroid cancer. Symptoms may include a lump in the neck, difficulty swallowing, or hoarseness.
Causes and Risk Factors
Thyroid disease can stem from various factors, including:
- Autoimmune Disorders: Conditions like Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease are leading causes.
- Genetics: A family history of thyroid issues increases risk.
- Iodine Imbalance: Too little or too much iodine can disrupt thyroid function.
- Stress: Chronic stress may exacerbate symptoms or trigger flare-ups in autoimmune thyroid conditions.
- Environmental Toxins: Exposure to certain chemicals or radiation can impair thyroid health.
- Gender and Age: Women are five to eight times more likely to develop thyroid disease, with risks increasing after age 40.
Diagnosis and Conventional Treatments
Diagnosing thyroid disease typically involves:
- Blood Tests: Measuring levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH), T3, T4, and thyroid antibodies.
- Imaging: Ultrasound or radioactive iodine scans to assess thyroid structure.
- Biopsy: Fine-needle aspiration for suspicious nodules.
Conventional treatments depend on the condition:
- Hypothyroidism: Synthetic thyroid hormone replacement (e.g., levothyroxine).
- Hyperthyroidism: Anti-thyroid medications, radioactive iodine therapy, or surgery.
- Goiter/Nodules: Monitoring, medication, or surgical removal.
- Thyroid Cancer: Surgery, radiation, or chemotherapy, depending on the type and stage.
While effective, these treatments may not address all symptoms, particularly fatigue, mood changes, or pain, prompting many to explore complementary therapies like acupuncture.
Acupuncture Treatment
Acupuncture, a cornerstone of Traditional Oriental Medicine (TOM), involves inserting thin, sterile needles into specific points on the body to balance the flow of energy. According to TOM, energy flows through meridians, and disruptions in this flow can lead to illness. Acupuncture aims to restore balance, reduce symptoms, and promote healing.
In modern practice, acupuncture is recognized for its ability to stimulate the nervous system, release endorphins, and regulate bodily functions. It is widely used for pain management, stress reduction, and treating chronic conditions, including thyroid disease.
How Acupuncture Can Help with Thyroid Disease
Acupuncture offers a holistic approach to managing thyroid disorders by addressing both physical symptoms and underlying imbalances. While it is not a cure for thyroid disease, research and clinical practice suggest it can:
- Regulate Hormone Levels: Acupuncture may influence the hypothalamic-pituitary-thyroid (HPT) axis, which controls thyroid hormone production.
- Reduce Inflammation: For autoimmune conditions like Hashimoto’s or Graves’ disease, acupuncture may modulate immune responses and reduce inflammation.
- Alleviate Symptoms: It can relieve fatigue, anxiety, palpitations, and muscle pain associated with thyroid disorders.
- Improve Energy and Mood: By stimulating endorphin release and reducing stress, acupuncture can enhance overall well-being.
- Support Conventional Treatments: Acupuncture may improve the effectiveness of medications or reduce their side effects.
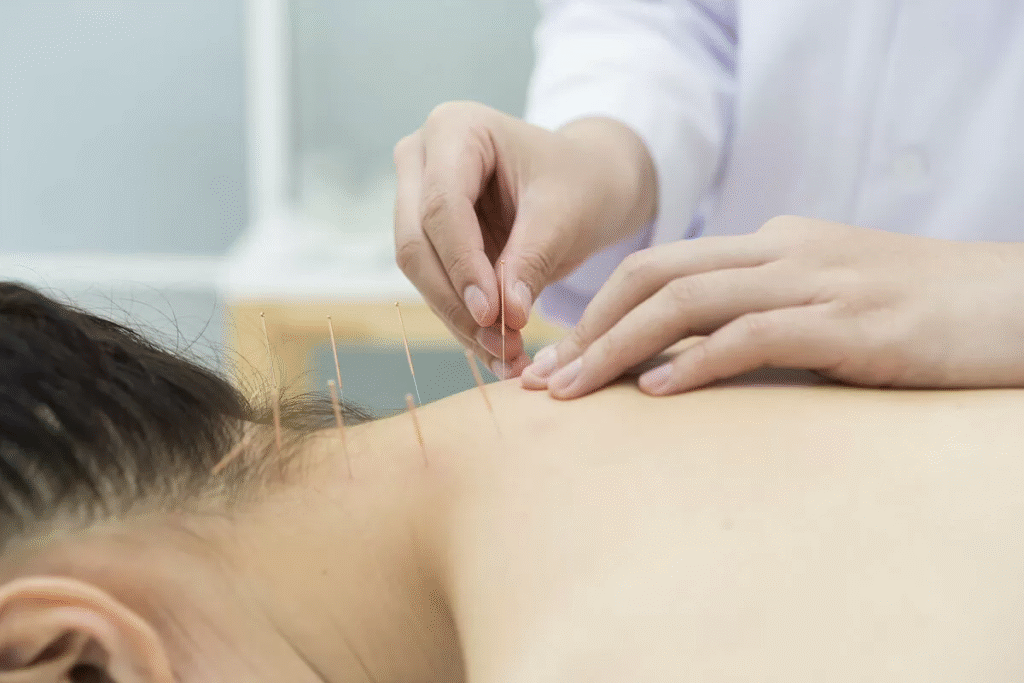
Scientific Evidence Supporting Acupuncture for Thyroid Disease
While large-scale clinical trials are limited, several studies highlight acupuncture’s potential benefits:
- A 2018 study in Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine found that acupuncture improved symptoms of hypothyroidism, such as fatigue and depression, in patients with Hashimoto’s thyroiditis.
- A 2020 review in Frontiers in Endocrinology suggested acupuncture may regulate TSH levels and improve quality of life in thyroid patients.
- Research in The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine (2019) indicated acupuncture reduced anxiety and palpitations in hyperthyroidism patients.
These findings, combined with anecdotal evidence, suggest acupuncture can be a valuable adjunct therapy, particularly for symptom management.
How Acupuncture Treats Thyroid Disease
In TOM, thyroid disorders are often linked to imbalances in specific organ systems, such as the Liver, Kidney, or Spleen, and disruptions in Energy or Yin-Yang balance. Acupuncture addresses these imbalances by targeting specific points to restore harmony and support thyroid function.
The TOM Perspective on Thyroid Disease
- Hypothyroidism: Often associated with “Kidney Yang Deficiency” or “Spleen Energy Deficiency,” leading to symptoms like fatigue, cold intolerance, and weight gain. Acupuncture aims to warm the body, boost Energy, and improve circulation.
- Hyperthyroidism: Linked to “Liver Fire” or “Yin Deficiency,” causing heat-related symptoms like sweating, anxiety, and palpitations. Acupuncture focuses on cooling the body and calming the nervous system.
- Goiter/Nodules: Viewed as “Energy Stagnation” or “Phlegm Accumulation.” Acupuncture promotes Energy flow and reduces stagnation.
The Acupuncture Process for Thyroid Disease
- Consultation: A licensed acupuncturist assesses the patient’s symptoms, medical history, and TOM diagnosis (e.g., pulse and tongue analysis).
- Treatment Plan: Sessions typically last 30–60 minutes, with 1–2 sessions per week for 6–12 weeks, depending on the condition’s severity.
- Needle Insertion: Thin needles are inserted into specific acupuncture points, often left in place for 15–30 minutes. Patients may feel a slight tingling or warmth.
- Adjunct Therapies: Some practitioners incorporate moxibustion (burning mugwort near acupuncture points), cupping, or herbal remedies to enhance effects.
Key Acupuncture Points for Thyroid Disease
Acupuncture points are selected based on the patient’s symptoms and TOM diagnosis. Below are some commonly used points for thyroid disorders, along with their locations and benefits:
LI4 (Hegu):
- Location: On the hand, between the thumb and index finger.
- Benefits: Relieves stress, boosts immunity, and promotes Energy flow. Often used for fatigue and headaches in hypothyroidism.
- Use Case: Helpful for both hypo- and hyperthyroidism to reduce general discomfort.
ST36 (Zusanli):
- Location: On the lower leg, about four finger-widths below the knee, outside the shinbone.
- Benefits: Strengthens the Spleen and boosts energy, addressing fatigue and digestive issues in hypothyroidism.
- Use Case: Commonly used for hypothyroidism to improve vitality.
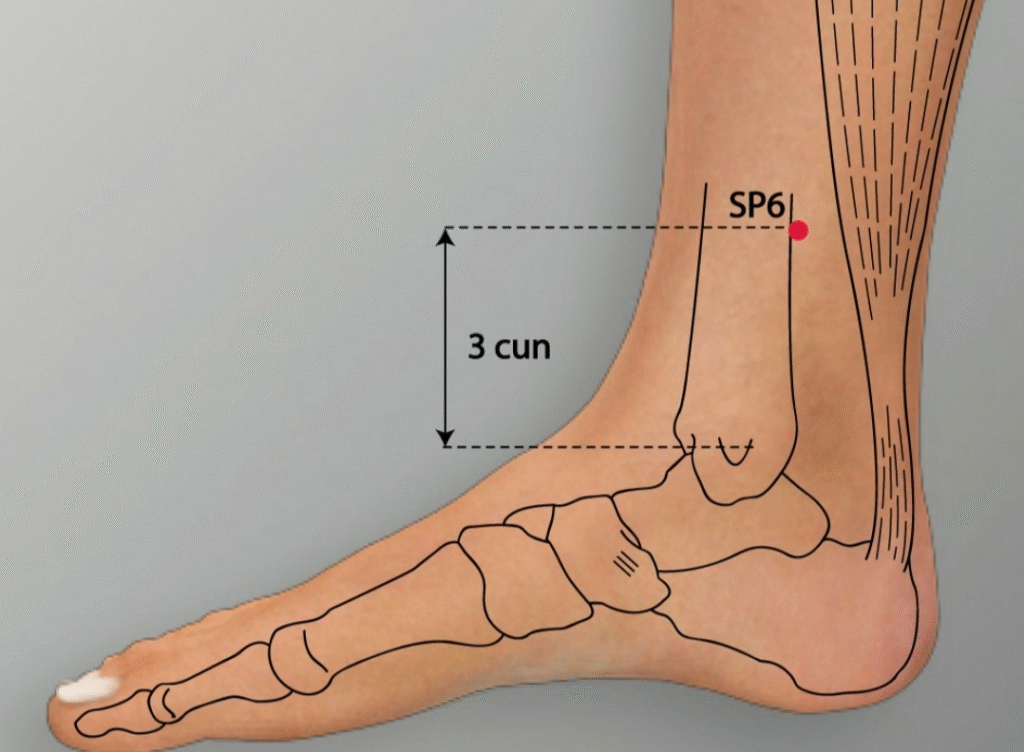
SP6 (Sanyinjiao):
- Location: On the inner lower leg, about four finger-widths above the ankle.
- Benefits: Nourishes Yin, regulates hormones, and supports the Spleen, Liver, and Kidney meridians. Effective for menstrual irregularities and fatigue.
- Use Case: Used for both hypo- and hyperthyroidism to balance hormones.
LV3 (Taichong):
- Location: On the foot, between the big toe and second toe.
- Benefits: Soothes Liver Energy, reduces stress, and calms anxiety or irritability in hyperthyroidism.
- Use Case: Ideal for hyperthyroidism symptoms like nervousness or palpitations.
KI3 (Taixi):
- Location: On the inner ankle, behind the medial malleolus.
- Benefits: Tonifies Kidney energy, supports hormonal balance, and alleviates cold intolerance in hypothyroidism.
- Use Case: Effective for hypothyroidism and fatigue.
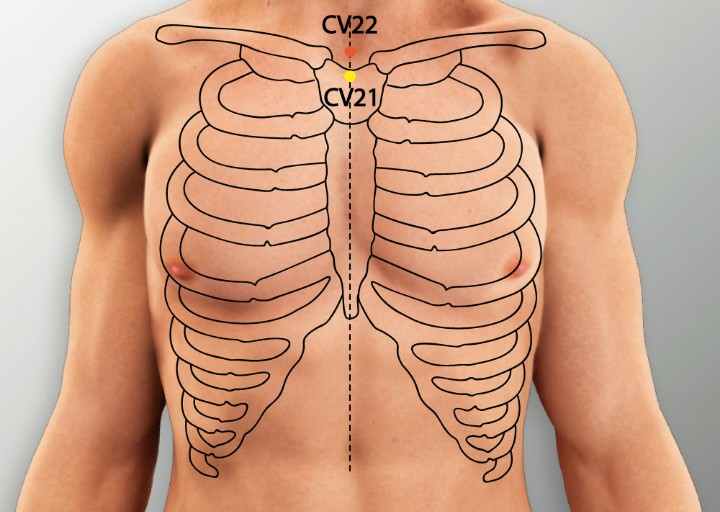
CV22 (Tiantu):
- Location: At the base of the throat, in the notch above the sternum.
- Benefits: Directly influences the thyroid gland, reduces swelling, and improves local circulation. Used for goiter or nodules.
- Use Case: Helpful for structural thyroid issues.
PC6 (Neiguan):
- Location: On the inner forearm, about two finger-widths above the wrist.
- Benefits: Calms the mind, reduces palpitations, and relieves anxiety in hyperthyroidism.
- Use Case: Effective for hyperthyroid symptoms like rapid heartbeat.
GV20 (Baihui):
- Location: At the top of the head, in the center.
- Benefits: Uplifts mood, clears brain fog, and balances energy. Useful for depression or mental fatigue in hypothyroidism.
- Use Case: Supports mental clarity in thyroid disorders.
Safety and Considerations
Acupuncture is generally safe when performed by a licensed practitioner. However, patients should:
- Choose a Qualified Acupuncturist: Ensure the practitioner is certified by a recognized body, such as the National Certification Commission for Acupuncture and Oriental Medicine (NCCAOM).
- Disclose Medical History: Inform the acupuncturist about thyroid medications, as acupuncture may enhance their effects.
- Monitor Symptoms: Acupuncture should complement, not replace, conventional treatments. Regular thyroid function tests are essential.
- Avoid Overstimulation: For hyperthyroidism, excessive stimulation of certain points may worsen symptoms, so a tailored approach is critical.
Benefits of Acupuncture for Thyroid Disease
Acupuncture offers several advantages as a complementary therapy:
- Holistic Approach: It addresses physical, emotional, and energetic imbalances, improving overall well-being.
- Minimal Side Effects: Unlike medications, acupuncture has few side effects, with mild soreness or bruising being rare.
- Personalized Treatment: Points and techniques are tailored to the individual’s symptoms and TOM diagnosis.
- Stress Reduction: By lowering cortisol levels, acupuncture can mitigate stress-related exacerbations of thyroid symptoms.
- Improved Quality of Life: Patients often report better energy, mood, and sleep after regular sessions.
Integrating Acupuncture with Conventional Care
For optimal results, acupuncture should be part of a comprehensive treatment plan. Patients should:
- Work with Their Doctor: Ensure acupuncture aligns with medical treatments, such as thyroid hormone replacement or anti-thyroid drugs.
- Maintain a Healthy Lifestyle: A balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management enhance acupuncture’s benefits.
- Monitor Progress: Regular blood tests and symptom tracking help assess the therapy’s impact.
Lifestyle Tips to Support Thyroid Health
In addition to acupuncture, the following can support thyroid function:
- Diet: Include iodine-rich foods (e.g., seaweed, fish) for hypothyroidism, but avoid excess iodine in hyperthyroidism. Selenium and zinc (found in nuts, seeds, and lean meats) support hormone production.
- Stress Management: Practices like yoga, meditation, or tai chi complement acupuncture’s stress-relieving effects.
- Sleep: Aim for 7–9 hours of quality sleep to support hormonal balance.
- Avoid Toxins: Limit exposure to endocrine-disrupting chemicals in plastics, cosmetics, or pesticides.
Conclusion
Thyroid disease, whether hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism, or structural abnormalities, can significantly impact quality of life. While conventional treatments remain essential, acupuncture offers a promising complementary approach by addressing symptoms, reducing stress, and supporting hormonal balance. Key acupuncture points like LI4, ST36, SP6, and CV22 target specific symptoms, providing relief for fatigue, anxiety, and other thyroid-related issues. By integrating acupuncture with medical care, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring, patients can achieve better symptom management and improved well-being.
If you’re considering acupuncture for thyroid disease, consult our licensed acupuncturist and your healthcare provider to create a personalized treatment plan. With its holistic benefits and minimal side effects, acupuncture may be a valuable addition to your thyroid health journey.
Fuji Wellness:
- Address: 132-0031 Matsushima 1-chome, 21-14, Tokyo, Japan
- Contact: Click here
- Email: sunnyphamsensei@gmail.com.
